Today I will show you how to build a simple volume controller using arduino and serial communication in GNU/Linux, specifically Debian Squeeze.
Arduino provides their own tool for serial communication but isn't practical for most applications because isn't customizable, although for debugging is well. Due to a college project I am studying about serial programming in order to establish communication with arduino from a program written in C. So far I am able to send and to retrieve data to and from arduino(duemilanove) and the first thing that came to my mind was to make a volume controller for my speakers :-). I hope you find it interesting!
Materials
- 1 Arduino(tested with Duemilanove)
- 1 potentiometer
- Wires
- C compilers and ncurses libraries, in debian:
apt-get install gcc libncurses5-dev
Let's get started
As first step, build the following circuit:
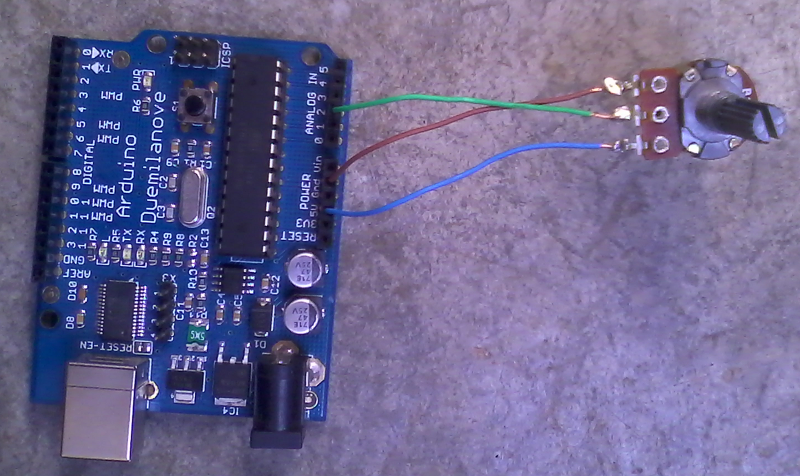
Figure 1. Circuit.
Use the following code for arduino to read the input from the potentiometer.
int input = 2;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
int value = analogRead(input);
int volumen = min(value/10, 100);
// The C program will read this value to change the volume
Serial.println(volumen);
delay(50);
}
This program reads the value that we indicate with the potentiometer(a value from 0 to 1023), then transform this value to a scale from 0 to 100, the volume of the speakers.
In the next program we establish serial communication with arduino, reads the appropiate values and and then, adjust the volume of the speakers using `amixer`.
// Compile with: gcc -Wall -o volume volume.c -lcurses
#include <ncurses.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <termios.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
char buffer[50];
struct termios tio;
int tty_fd, volumen, i;
char v, ch[2];
char *device = "/dev/ttyUSB0";
memset(&tio,0,sizeof(tio));
tio.c_iflag = 0;
tio.c_oflag = 0;
tio.c_cflag = CS8 | CREAD | CLOCAL;
tio.c_lflag = 0;
tio.c_cc[VMIN] = 1;
tio.c_cc[VTIME] = 5;
tty_fd=open(device, O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
cfsetospeed(&tio, B9600);
cfsetispeed(&tio, B9600);
fcntl(STDIN_FILENO, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
tcsetattr(tty_fd, TCSANOW, &tio);
volumen = 0;
initscr();
while (ch[0] !='q') {
read(STDIN_FILENO, ch, 1);
if (read(tty_fd,&v,1) > 0) {
if (v == '\n') {
sprintf(buffer, "amixer --quiet set Master %d%%", volumen);
system(buffer);
printw("[");
for (i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (i < volumen)
printw("#");
else
printw(".");
}
printw("] %d%%", volumen);
refresh();
clear();
volumen = 0;
} else {
if (v >= '0' && v <= '9')
volumen = volumen * 10 + (v - '0');
}
}
}
endwin();
close(tty_fd);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Connect the USB cable from arduino to the computer and execute the previous program and we get:
That is all friends! See you in the next post.
References
| 1 | Serial Programming/Serial Linux |
| 2 | Reading a Potentiometer (analog input) |